
As cloud computing continues to evolve, businesses are finding that their initial cloud choices may no longer meet their needs. Whether it's to optimize performance, reduce costs, or enhance security, transitioning from one cloud provider to another has become an essential business strategy.
Moreover, different cloud providers offer unique pricing structures and performance capabilities – a company might use AWS for compute-heavy workloads while leveraging Google Cloud’s AI/ML capabilities or Azure for enterprise integrations. Migration flexibility allows them to choose the best provider for each workload and ensures businesses aren't trapped in one ecosystem and can switch providers if needed.
However, cloud-to-cloud migration involves complex challenges that require careful planning, execution, and ongoing optimization. To help make the path to cloud efficiency more clear, we explore the essentials of cloud-to-cloud migration, the common obstacles organizations face, and best practices to ensure a smooth transition in our latest blog.
Understanding Cloud-to-Cloud Migration
Cloud-to-cloud migration refers to transferring applications, data, and workloads from one cloud provider to another without moving to an on-premises infrastructure. Companies opt for this migration for several reasons, including better service offerings, compliance requirements, cost management, or to avoid vendor lock-in.
Businesses generally operate within one of the following cloud models:
- Single Cloud Provider: Relying on one cloud service provider for all computing needs.
- Multi-Cloud: Using multiple cloud providers to distribute workloads and minimize risks.
- Hybrid Cloud: Integrating public and private clouds to achieve a balance of security and scalability.
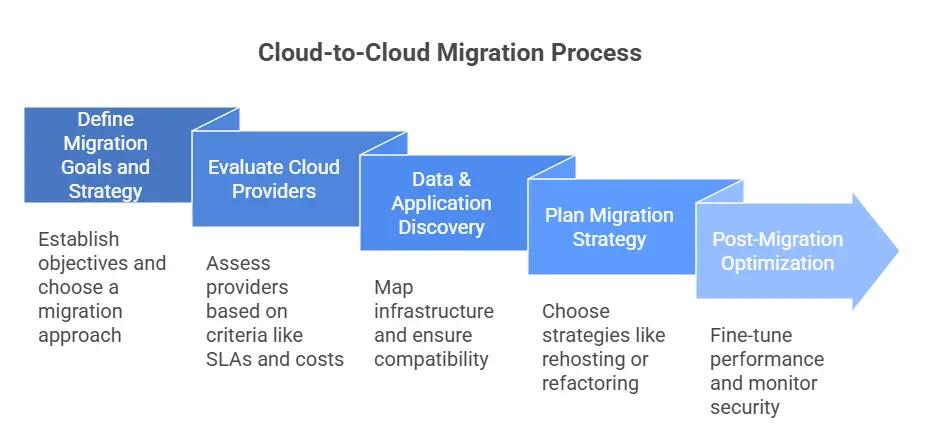
Cloud to Cloud Migration, Step by Step
Regardless of which route your organization chooses, the steps for cloud-to-cloud migration are fairly similar across single-cloud, multi-cloud, and hybrid-cloud strategies because the fundamental process of moving workloads remains the same.
Define Migration Goals and Strategy
It all starts with assessment and planning, where companies evaluate their existing workloads, dependencies, security requirements, and costs. Regardless of the cloud strategy, understanding which applications or data need to be migrated, estimating downtime, and identifying performance needs are essential. To put it simply, before initiating a migration, organizations should clearly define their objectives. Based on these goals, they can choose a migration strategy such as:
- Replication: Copying data and applications without altering them.
- Re-architecting: Modifying workloads to better align with the new cloud’s capabilities.
- Replacement: Switching to a different cloud-native solution entirely.
Evaluate Cloud Providers
Once you establish the necessary criteria, evaluating cloud providers based on these criteria is a crucial step in ensuring a successful migration, as different providers offer varying capabilities, pricing structures, and levels of support. A thorough evaluation involves analyzing several key factors to determine the best fit for your workloads and business needs. Some factors include:
- Service-level agreements (SLAs) and support offerings.
- Compliance and regulatory adherence.
- Integration with existing tools and services.
- Cost structure and potential hidden fees.
Data & Application Discovery
Next comes data and application discovery, where companies map out their infrastructure and ensure compatibility between the source and target clouds. This process includes identifying interdependencies between applications, networking configurations, and storage needs. Whether a business is moving everything from one cloud provider to another or spreading workloads across multiple providers, this step ensures a smooth transition. Key steps include:
- Data Mapping: Identifying dependencies and structuring data for transfer.
- Testing Environment: Creating a staging environment to validate the migration.
- Incremental Rollout: Moving workloads in phases to minimize disruptions.
Planning Migration Strategy
Once the environment is understood, planning migration strategies like rehosting (lift-and-shift), refactoring, or re-platforming is chosen based on business needs. Additionally, data transfer follows, using tools like cloud-native migration services, third-party solutions, or custom pipelines to move workloads securely and efficiently. Testing is also a crucial component that comes before full deployment, ensuring applications work correctly in the new cloud environment.
Post-Migration Optimization
Finally, optimization and monitoring must take place after a successful migration. Regardless of the cloud strategy, companies must fine-tune performance, optimize costs, and establish monitoring for security and compliance. These steps remain consistent across single-cloud, multi-cloud, and hybrid setups because they address core migration challenges like data integrity, application performance, and operational continuity. Continuous monitoring ensures:
- Security protocols are updated.
- Performance meets operational requirements.
- Costs are managed effectively using cloud monitoring tools.
Common Challenges in Cloud-to-Cloud Migration
Migrating workloads between cloud providers comes with a set of challenges that organizations must proactively address to ensure a smooth and cost-effective transition. While the benefits of cloud migration include flexibility, resilience, and cost optimization, businesses often encounter security risks, performance inconsistencies, and unexpected costs that can impact operations if not managed properly.
Security and Compliance Risks
Moving data between cloud providers introduces security vulnerabilities, especially when handling sensitive information such as customer records, intellectual property, or regulated financial and healthcare data. Organizations must enforce end-to-end encryption both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access. Strong identity and access management (IAM) policies should be in place to ensure that only authorized users can access migrated data. Compliance with industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, or ISO 27001 is crucial, requiring careful monitoring of where data is stored and how it is processed in the new cloud environment. Businesses should also implement continuous security assessments and logging to detect and mitigate potential breaches during and after migration.
Performance Variations
Different cloud providers have unique architectures, hardware configurations, and network infrastructures, which can lead to unexpected performance variations when applications are migrated. Workloads that run efficiently in one cloud may experience latency issues, slower response times, or increased resource consumption in another due to differences in virtualization, storage performance, or networking. Organizations need to benchmark workloads before migration and optimize applications for the new environment. This may involve reconfiguring databases, adjusting autoscaling policies, or fine-tuning compute and memory allocations to align with the target cloud’s infrastructure. A robust testing phase should be included in the migration strategy to detect performance bottlenecks before full deployment.
Unexpected Costs
Cloud-to-cloud migration often results in hidden expenses that can inflate overall costs if not anticipated. Cloud providers charge data egress fees, meaning businesses may incur significant costs when transferring large datasets from one cloud to another. Additionally, licensing differences between cloud providers can lead to unexpected expenses, especially when using proprietary software or third-party services with cloud-specific pricing models. Misconfigurations in the new cloud environment, such as over-provisioning resources or inefficient storage choices, can further drive up operational expenses. To avoid budget overruns, organizations should conduct a cost analysis, leverage cost-optimization tools, and explore pricing models such as reserved instances or committed-use discounts to reduce long-term expenses.
Best Practices for a Successful Migration
Prioritize Security at Every Stage
Security should be embedded into every phase of cloud-to-cloud migration, from planning to post-migration operations. Before initiating migration, businesses must conduct a comprehensive security assessment to identify risks, such as data exposure, misconfigurations, and compliance gaps. End-to-end encryption should be enforced both in transit and at rest to protect sensitive data during the transfer process. Role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be implemented to prevent unauthorized access, ensuring that only authorized personnel can interact with critical resources. Organizations must also comply with industry-specific security frameworks, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, ensuring that data governance policies remain intact during and after migration. Continuous logging and threat monitoring should be in place to detect anomalies and mitigate security breaches in real time.
Use Automation to Streamline Migration
Migrating workloads manually can be complex, error-prone, and time-consuming, making automation a key factor in a successful cloud transition. Businesses should leverage cloud-native migration tools, Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC), and orchestration platforms to automate data transfers, application deployments, and infrastructure configurations. Automated scripts can ensure consistency across cloud environments, reducing human errors that could lead to performance bottlenecks or security vulnerabilities. Tools like Terraform, Ansible, or Kubernetes can help automate provisioning and deployment, while data replication and synchronization tools like AWS DataSync, Azure Migrate, and Google Transfer Appliance facilitate faster and more reliable migrations. By automating workflows, organizations can minimize downtime, accelerate transition times, and improve overall migration efficiency.
Continuously Monitor and Optimize
Once migration is complete, ongoing monitoring and optimization are essential to maintain performance, security, and cost efficiency. Cloud providers offer built-in monitoring and observability tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Operations Suite to track resource utilization, latency, and potential security threats. Organizations should actively monitor application performance metrics, network traffic, and storage costs to identify inefficiencies and optimize resource allocation. Implementing automated scaling policies ensures that workloads dynamically adjust based on demand, preventing over-provisioning and unnecessary cloud expenses. Additionally, businesses should conduct regular security audits and vulnerability scans to detect potential threats and ensure compliance with evolving regulations. Continuous fine-tuning of workloads and infrastructure configurations will maximize efficiency and long-term success in the new cloud environment. Read our latest blog: Migration as a Service (MaaS) vs Self-Migration.
Real-World Case Studies: Cloud to Cloud Migration in Action
Successful migrations aren’t just theory; they’re happening across industries today. The following examples highlight how organizations partnered with Wanclouds to overcome challenges, minimize downtime, and achieve secure, cost-effective transitions between cloud environments.
Case Study: Tekrom’s Zero-Downtime Migration
A strong example of cloud-to-cloud migration comes from Tekrom Technology, a leading e-commerce solutions provider. Tekrom needed to move more than 100 virtual machines from IBM Cloud Classic to VMware vCenter Server (VCS) on IBM Cloud, without impacting business operations.
With Wanclouds’ VPC+ automation platform, the migration was fully orchestrated and executed seamlessly, ensuring zero downtime and a smooth transition to the new environment.
Key Outcomes:
- Migrated 109+ virtual machines with no service disruption.
- Redesigned network infrastructure, including routing and firewall policies.
- Leveraged automation to reduce manual errors and accelerate the process.
- Saved significant time and costs compared to traditional migration methods.
Tekrom’s success shows how businesses can leverage Wanclouds’ expertise and automation tools to carry out complex migrations quickly, securely, and without disrupting critical services.
Quotes Success:
“Wanclouds delivered our project without any problems... and saved us a lot of cost and time.” — Huseyin Cengiz, DevOps Team Lead, Tekrom Technology
Discover how Wanclouds helped Tekrom migrate from IBM Classic to VMware with ease and efficiency.
Case Study: Tamkeen’s Hybrid Cloud Journey
A great example of successful cloud-to-cloud migration comes from Tamkeen, a leading public authority that empowers Bahrain’s private sector. Tamkeen needed to modernize its IT infrastructure by moving workloads from legacy systems into a secure, scalable cloud environment.
With Wanclouds’ expertise, Tamkeen adopted a hybrid cloud approach, seamlessly migrating workloads into IBM Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) while ensuring that critical services remained available throughout the transition.
Key Outcomes:
- Migrated critical workloads without disruption.
- Enhanced scalability and security by leveraging a hybrid setup.
- Maintained compliance and governance requirements during migration.
- Gained flexibility to optimize costs and adapt services dynamically.
Tamkeen’s success demonstrates that with the right partner, businesses can overcome migration challenges and unlock the full benefits of multi- and hybrid-cloud strategies.
Quotes Success:
“By partnering with Wanclouds, Tamkeen successfully transitioned to a hybrid cloud setup, ensuring business continuity, compliance, and scalability while preparing for future digital growth.”
Why Wanclouds is the Right Partner for Your Cloud-to-Cloud Migration
Migrating workloads between cloud providers is a challenging task, but Wanclouds simplifies the process with:
- End-to-End Cloud Expertise: From assessment to optimization, Wanclouds ensures smooth transitions.
- Multi-Cloud Support: Tailored solutions for AWS, Google Cloud, and other leading providers.
- Cost Optimization Strategies: Helping businesses reduce waste and maximize cloud investments.
- Advanced Automation Tools: Minimizing downtime and securing data integrity.
- Proven Track Record: Trusted by businesses for secure and efficient cloud transitions.
By adopting a structured approach, leveraging automation, and working with experienced partners like Wanclouds, organizations can achieve a seamless transition and unlock the full potential of their cloud environments.
Looking to migrate to a new cloud provider? Contact Wanclouds today to get started on your cloud-to-cloud migration journey.