Avoiding vendor lock-in is undoubtedly the most frequently cited reason for adopting a Multi-Cloud strategy, among the many other benefits associated with it. Since a Multi-Cloud approach is based on the use of multiple Cloud services hosted by different private and public cloud providers, companies use Multi-Cloud environments to distribute computing resources and minimize the risk of downtime and data loss. In a recent State of the Cloud survey, more than 80% of enterprises reported medium to high levels of concern about being locked into a single public cloud platform.
An enterprise's perception of vendor lock-in depends entirely on its goals. For some enterprises, avoiding a vendor lock-in is a core business requirement or a way to achieve greater portability for their applications. With such portability, it gets easier for them to move applications to and across platforms. More and more enterprises are finding the Multi-cloud approach to be the most optimal for their businesses, particularly in situations like vendor lock-in.

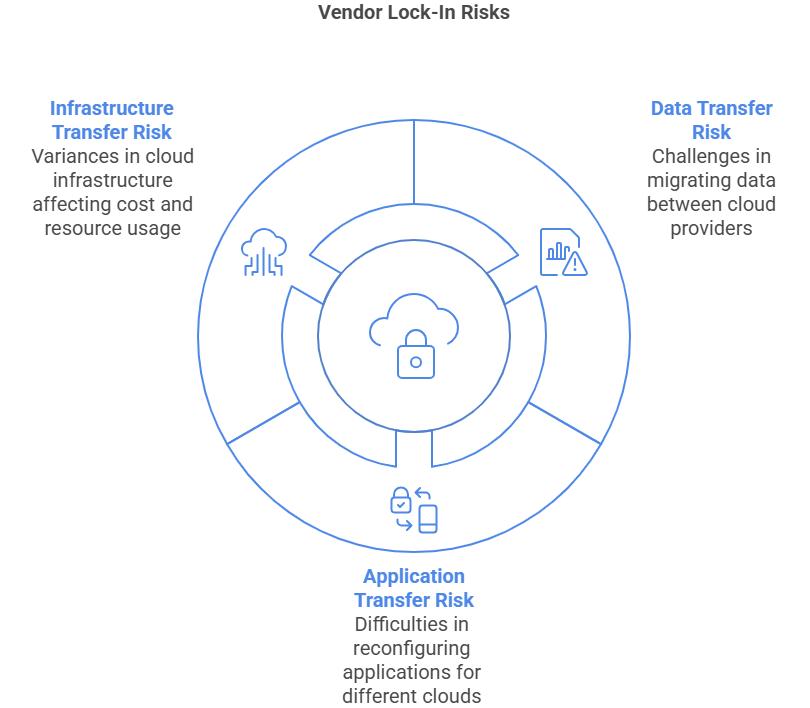
Risks Associated with Vendor Lock-In
The following are the primary Vendor Lock-In risks that are involved in working with a single Cloud provider, which make it difficult for you to migrate across multiple Clouds:
Data Transfer Risk
Migrating all your data from one Cloud Service Provider to another is not straightforward, as it involves numerous risks and multiple factors that must be considered. These include suitable and reliable data extraction methods, maintaining data integrity, data translation, transferring data without compromising the application’s functionality, and conducting time and cost analyses.
Application Transfer Risk
The risk of reconfiguring applications that run in your current environment and running them natively on another provider can be an extremely complex and challenging process. One of the main reasons for this difficulty and complexity is the lack of standard interfaces and open APIs, as every Cloud Service Provider has its own specifications and standards, which make it very challenging to migrate from one CSP to another.
Infrastructure Transfer Risk
Every major cloud service provider does things differently in terms of offerings and pricing plans. For example, their virtual machines (VMs) and associated pricing may vary from those of other vendors, and their database offerings and formats may differ as well. This makes it difficult to ensure that you have the appropriate resource usage and cost savings when switching providers. This requires proper planning & detailed assessment to help you choose the suitable cloud for your applications.
Significance of Multi-Cloud Architecture
With a Multi-Cloud architecture implemented, enterprises can distribute their workloads across multiple cloud environments to maximize efficiency while mitigating risks associated with individual Cloud environments. This value proposition alone is enough to justify the widespread growth and adoption of Multi-Cloud infrastructure solutions among enterprises in the near future.
Optimized IT Spend
Every Cloud is built differently. These differences extend not only to physical infrastructure components but also encompass a diverse range of characteristics, pricing models, and policies, among other aspects. Therefore, the right fit is determined based on each metric for individual apps and specific business needs. This results in compromised choices and unnecessary tradeoffs.
A Multi-cloud infrastructure offers a rich set of Cloud options to solve your needs across a diverse range of computing and business functions, thereby optimizing returns on Cloud investments. Therefore, in a multi-cloud environment, you have the liberty to choose whatever cloud resources are being offered without having to compromise on any of your choices.
A More Secure and Less Prone Environment
Since your infrastructure is hosted by vendors with multiple data centers within each geographic region, any outages that occur can cause significant disruptions on your end. However, with a Multi-Cloud environment implemented, you have independent copies of your workloads on other Cloud servers, which can be deployed without causing any disruption on your end in case of an outage. This way, you can minimize the risk of your business being affected.
Additionally, a Multi-Cloud environment enables enterprises to maintain a secure and cost-effective environment that combines both security and cost savings. The most critical and security-focused applications are kept in the private Cloud, while the regular business data and applications are kept in cost-effective public cloud networks.
High Accessibility and Low Latency
Accessing data and apps stored at distant locations across the Cloud network is not instantaneous. The data travels across several nodes before reaching end-users, resulting in minor delays. Such latency issues caused by data traveling significant distances can be easily avoided by adopting a Multi-Cloud infrastructure.
Using multiple vendors helps achieve faster speeds and improves the application's user experience, as the data center closest to end-users can serve the respective data request with minimal server hops. This capability is crucial and highly valuable for global enterprises that need to access and manage corporate data across geographically dispersed locations while maintaining a seamless and consistent end-user experience.
How Wanclouds Multi-Cloud Strategy Helps You Avoid Vendor Lock-In
Wanclouds Multi-Cloud Migrations as a Service, powered by our VPC+ platform, simplifies and accelerates your journey to a Multi-Cloud environment, ensuring you avoid the pitfalls of vendor lock-in. Our automated, fully-managed solution enables seamless migration of workloads, applications, and data across cloud providers, offering cross-cloud portability and reducing the complexities of data, application, and infrastructure transfers. With Wanclouds, you gain the flexibility to choose the best Cloud for your needs without being tied to a single provider.
- Seamless Automation: Automate discovery, translation, and migration of workloads with VPC+, eliminating manual processes and reducing migration time from weeks to hours.
- Cross-Cloud Portability: Migrate applications and data between clouds effortlessly, ensuring flexibility and avoiding dependency on a single provider.
- Cost Optimization: Pay-as-you-migrate model and optimized resource allocation reduce costs and eliminate the need for expensive consultants.
- Comprehensive Migration Coverage: Migrate VPCs, VMs, databases, and more, with ongoing support to ensure post-migration success.
- Disaster Recovery: Use VPC+ DRaaS to back up and restore Multi-Cloud infrastructure across regions or providers, enhancing business continuity.
Take the Next Step:
Ready to embrace a Multi-Cloud strategy and avoid vendor lock-in? Contact Wanclouds today by filling out our Request Form or contact one of our sales representatives at [email protected].